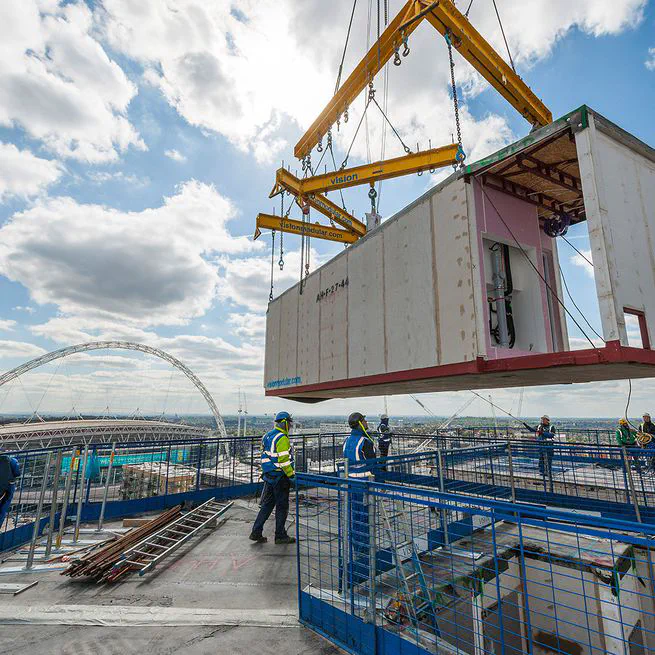

Summary: Offsite construction (OSC) is a promising solution to address the housing affordability and supply challenge in New Zealand (NZ). However, most OSC is still ‘new’ and untested in NZ and cannot effectively reduce costs, time and risks, which hinders the broader use of OSC across the country. It has been revealed both in the literature and by interviewing industry experts that OSC knowledge learnt from previous projects is highly valuable to new projects; however, currently the designers, engineers and contractors do not effectively capture and reuse knowledge from existing projects. In this project, we propose to affect industry-wide behaviour change for capturing and reusing OSC knowledge, through developing an open OSC knowledge base, a best practice guideline and multiple case studies. Additionally, a longitudinal survey will be conducted to evaluate how effective the proposed knowledge base and guideline can affect OSC professionals’ behaviour change on knowledge reuse. Funder: Building Research Association of New Zealand (BRANZ) Team: Yang Zou (PI), Johannes Dimyadi (Codify Asset Solutions), Brian H.W. Guo (University of Canterbury), Roy Davies (University of Auckland), Lixin Jiang (University of Auckland) Duration: 2023-2025
Jan 1, 2023

Summary: The rail digital twin can incorporate advanced technology such as AI-based computer vision to detect cars on the track (as shown in the inset), implement how this information would affect the rail operation (such as triggering signal lights as shown) and determine how the autonomous rail car would then respond (e.g. by slowing down to give the car time to exit the track or coming to a complete halt before the rail crossing).Hence the digital twin can be used to assess the full operational viability of the autonomous rail car before future investment in a real-world pilot. Funder: New Zealand Transport Agency (NZTA) Innovation Fund through Reureu Kotahitanga Ltd (RKL) Team: Yang Zou (PI), Michael O’Sullivan (University of Auckland), Zhengxing Chen (University of Auckland), Graeme Everton (RKL) Duration: 2023
Jan 1, 2023

Summary: Smart construction is the second research program that we have in our Construction 4.0 research programme. This program will investigate the intrinsic properties and invariant signatures of construction objects, such as footings, slabs, beams etc, as well as their synergistic structural performance, to create a new end-to-end computational platform for design and manufacture. This opens the door to full automation of prefabrication and modularisation, which will significantly improve building performance, environmental profile and productivity in the sector. The platform we develop in this program will be able to analyse planning for building product/system manufacturing and construction projects. It will create optimised solutions for constructability of buildings taking the near real-time capacity and capability in a value chain process. Building product manufacturers, suppliers, builders, contractors and subcontractors will be able to better plan for new projects and prioritise resources. Change will likely be seen in business models in the construction sector and improved efficiency in adoption of new technologies. Funder: New Zealand Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment (MBIE) Endeavour Fund (Research Programme) Team: Alice Chang-Richards (PI; University of Auckland), Yang Zou, Yuqian Lu (University of Auckland) Duration: 2022-2026 This is an external link to the research programme from Heavy Engineering Research Association (HERA)
Jan 1, 2022
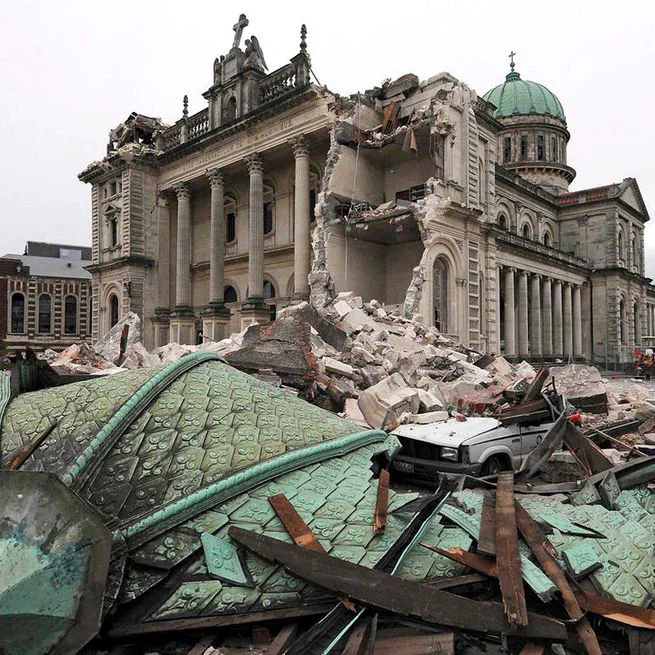

Summary: Fast search & rescue (S&R) and emergency assessment of building conditions are critical in the case of major earthquakes. Current practices are, however, often conducted by human, which is labour intensive, dangerous and subject to errors. The project aims to analyse the feasibility of developing an intelligent robotic system prototype that can perform efficient post-earthquake S&R and emergency assessment of building conditions by applying various state-of-art digital technologies. It focuses on understanding New Zealand needs and testing technologies to develop an overall framework for the proposed robotic system. Funder: Building Research Association of New Zealand (BRANZ) Team: Yang Zou (PI), Jason Ingham (University of Auckland) Duration: 2020
Jan 1, 2020
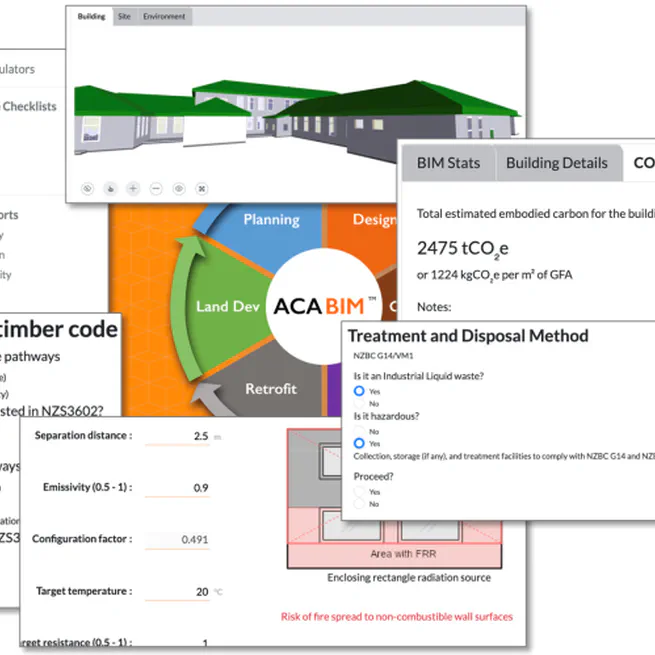
Summary: Prefabricated building is a promising solution to address the housing affordability and supply challenge in New Zealand (NZ). However, the current audit of prefabricated buildings for compliance with Building Code follows a manual, error-prone and time-consuming process, leading to the challenge of meeting timely delivery expectations. In recent years, some automation efforts have been observed internationally to improve the productivity and performance of Building Code compliance processes. We propose to investigate what lessons NZ can learn from these international efforts. The project aims to identify key barriers and provide recommendations for adopting automated Building Code compliance checking for prefab designs in NZ. It will carefully analyse selected international and NZ cases that deliver automated Building Code compliance checking and focus on transferring evidence-based knowledge and experience to NZ. To validate the proposed recommendations, it will then implement the latest automated code checking technologies on two real NZ prefab designs. Funder: Building Research Association of New Zealand (BRANZ) Team: Yang Zou (PI), Johannes Dimyadi (Codify Asset Solutions), Brian H.W. Guo (University of Canterbury), Eleni Papadonikolaki (UCL) Duration: 2019-2022 This is an external link to the research project in Build Magzine
Jan 1, 2019
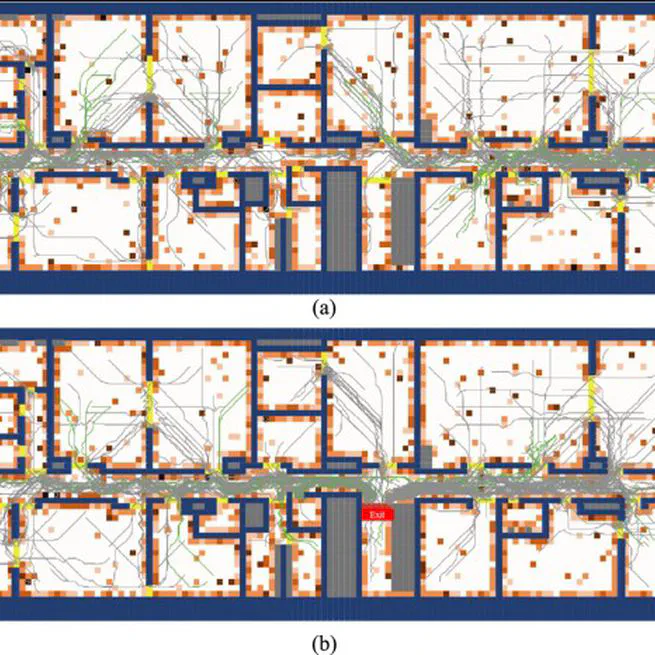
Summary: Developing a simulation framework that considers how people behave during post-earthquake evacuations. It will consider human behaviours such as decision making and psychological/social patterns. The project aims to have a more human-centred design of buildings, where not only the mechanical and functional properties of a building matter in the design process, but also human behaviour. Ultimately, the simulation framework is used to predict how an evacuation will go when the building design is modified using human behaviour as input and can be improved before a building is constructed and occupied. Funder: New Zealand Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment (MBIE) National Science Challenge (NSC) – Science for Technological Innovation (SfTI) Team: Vicente Gonzalez (PI; University of Auckland), Yang Zou, Jiamou Liu(University of Auckland) Duration: 2019-2022
Jan 1, 2019
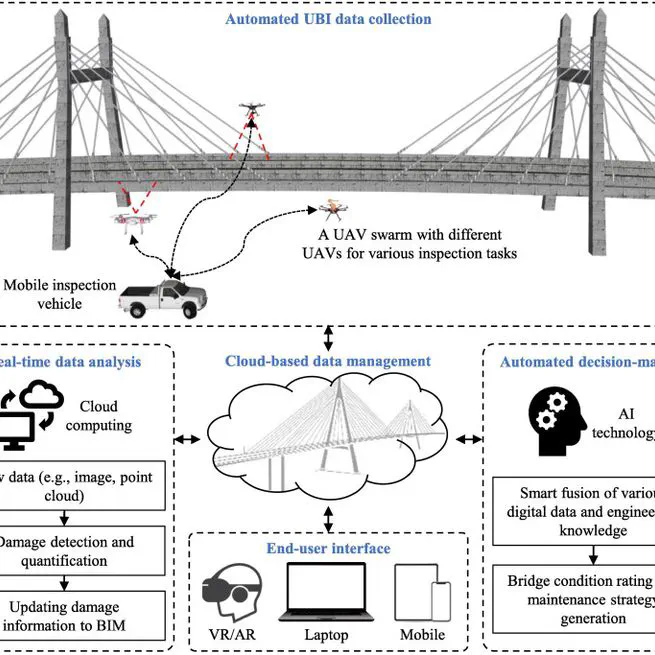
Summary: In the aftermath of major earthquakes, rapidly capturing and quantifying the extent and severity of damage on buildings and critical infrastructure plays an important role in post-earthquake operations such as search and rescue, emergency repairs and long-term reconstruction. Current damage assessment practices, however, are labour intensive, time consuming and subject to errors, which also raise safety concerns for those engineers undertaking the inspections. To overcome this challenge, this project aims to develop a rapid, automated and data-driven method for post-earthquake bridge inspection by using Building Information Modelling (BIM) and 3D reconstruction. New algorithms are developed to reconstruct and analyse as-damaged bridge BIM to identify bridges’ damage grade and support decision making. To support further analysis, an Information Interpretation Engine (IIE) is developed to transform as-damaged BIM data to engineering analysis applications. Success of this project will not only add fundamental knowledge to post-earthquake damage assessment but significantly improve current engineering practice in New Zealand and worldwide. Funder: University of Auckland Faculty Research Development Fund (FRDF): New Staff Grant Team: Yang Zou (PI), Vicente Gonzalez (University of Auckland), James Lim (University of Auckland) Duration: 2019-2022
Jan 1, 2018